About Domain
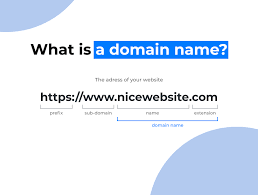
A domain name is a human-readable address for a website, like “example.com”, that translates to a numerical IP address, making it easier for users to find and access websites.
Here’s a more detailed explanation:
What it is:
A domain name is the address you type into a web browser to visit a specific website.
How it works:
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses, which computers use to communicate.
Why it’s important:
Domain names are easier to remember and type than IP addresses, which are long strings of numbers.
Examples:
google.com
wikipedia.org
example.com
Domain Name vs. URL:
While related, a domain name is the main part of a website’s address (like “example.com”), while a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) includes the entire address, including the protocol (http or https) and the specific webpage or resource (like https://www.example.com/about).
Subdomains:
A subdomain is a domain that’s part of a larger domain (e.g., mail.google.com is a subdomain of google.com).
Registration:
You can register a domain name through a domain registrar and pay an annual fee to maintain ownership.



 >
>





Leave a Reply